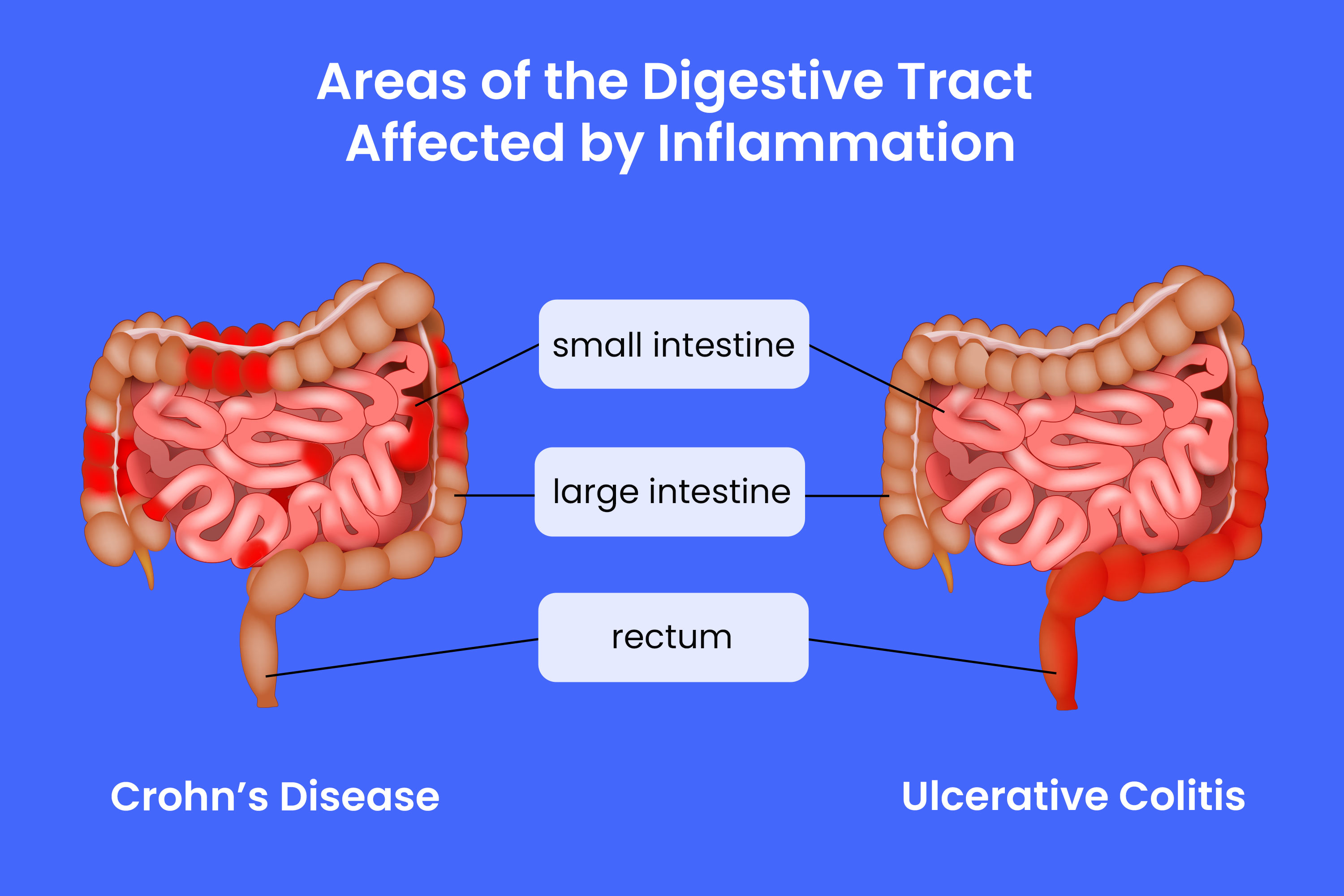
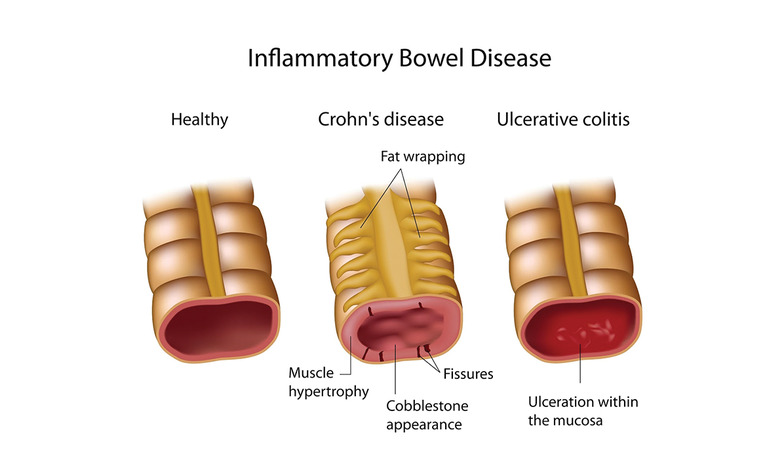
CROHN’S DISEASE
Crohn’s disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. It can affect any part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, from the mouth to the anus, but it most commonly affects the small intestine and colon.
Causes & Risk Factors
The exact cause is unknown, but factors that may contribute include:
- Genetics – Family history increases risk.
- Immune System – An overactive immune response may attack the digestive tract.
- Environmental Factors – Diet, smoking, and stress can trigger flare-ups.
Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease
Symptoms vary depending on the affected area and severity but commonly include:
- Chronic diarrhea (may be bloody)
- Abdominal pain (cramping or severe)
- Weight loss & malnutrition
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Mouth sores
- Fistulas & abscesses (painful infections, especially around the anus)
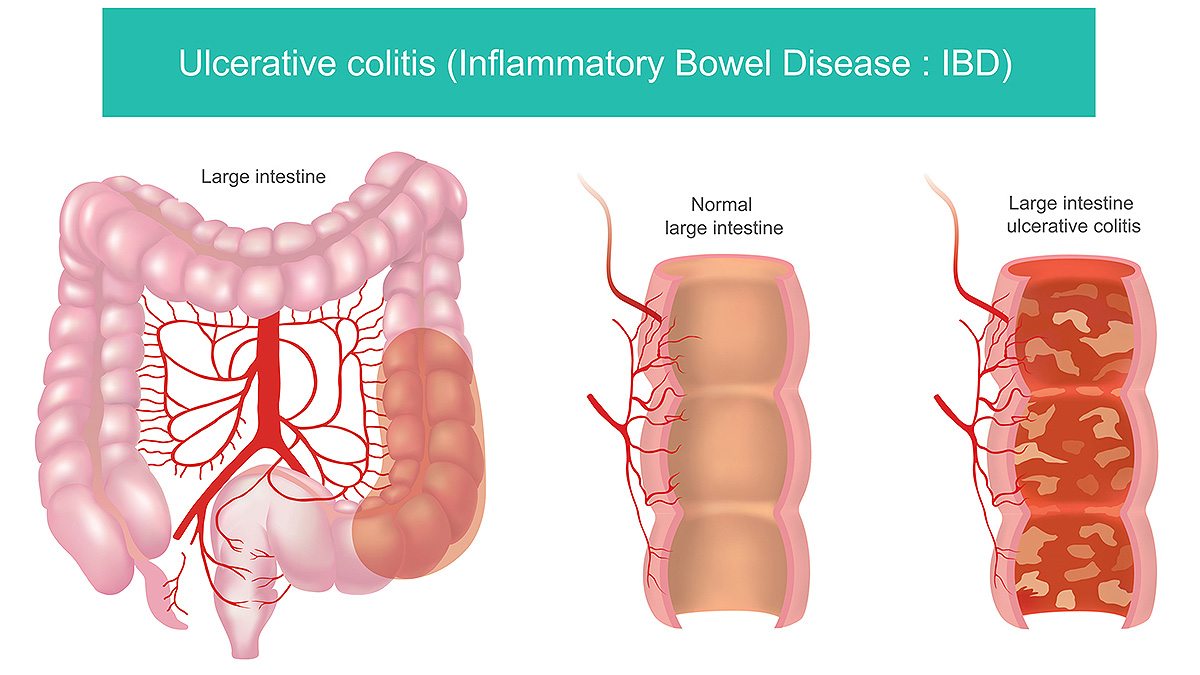
ULCERATIVE COLITIS(UC)
Ulcerative Colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes long-term inflammation and ulcers (sores) in the colon (large intestine) and rectum. Unlike Crohn’s disease, which can affect any part of the digestive tract, UC is limited to the colon and rectum and affects only the inner lining of the bowel.
Causes & Risk Factors
-
Immune System Dysfunction – The body mistakenly attacks the colon’s lining.
- Genetics – Family history increases the risk.
- Environmental Triggers – Stress, diet, and infections may worsen symptoms.
Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis
-
Frequent, bloody diarrhea (sometimes with mucus)
- Abdominal pain & cramping
- Urgency to defecate (tenesmus)
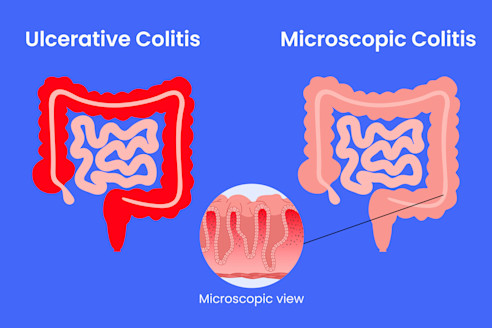
MICROSCOPICCOLITIS
Microscopic Colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes persistent watery diarrhea but without visible damage to the colon during a colonoscopy. It is only diagnosed through a biopsy, where inflammation is seen under a microscope.
Causes & Risk Factors
-
Autoimmune Disorders (common in people with celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis, thyroid disorders).
- Chronic NSAID or Aspirin Use (can irritate the colon).
- Certain Medications (e.g., proton pump inhibitors, antidepressants, statins).
- Bacterial or Viral Infections (may trigger inflammation).
- Smoking (increases risk).
What are the symptoms?
-
Chronic, watery diarrhea (without blood)
- Frequent bowel movements (5–10 times per day)
- Abdominal pain & cramping
- Weight loss & fatigue
- Nausea
INDETERMINATECOLITIS
Indeterminate Colitis (IC) is a type of Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) where doctors cannot clearly classify whether the inflammation is due to Crohn’s Disease or Ulcerative Colitis (UC). It is usually diagnosed when colonoscopy and biopsy results show mixed features of both conditions.
Causes & Risk Factors
- Genetics (family history of IBD)
- Immune System Dysfunction
- Environmental Triggers (diet, infections, smoking)
Symptoms of Indeterminate Colitis
- Chronic diarrhea (may or may not have blood)
- Abdominal pain & cramping
- Weight loss & fatigue
- Urgency to defecate
- Fever (during flare-ups)/li>
- Anemia (due to blood loss)



